# DRAG IN AIRCRAFT:
Table of Contents:
- What Is Drag In Aircraft?
- Types Of Drag In Aircraft
- Parasitic Drag
Form Drag
Interference Drag
Skin Friction Drag - Induced Drag
- Wave Drag
What Is Drag In Aircraft?
In aerodynamics, the drag in aircraft refers to the force that opposes forward motion through the atmosphere and is parallel to the direction of the free-stream velocity of the airflow. Drag is a mechanical force. It is generated by the interaction and contact of a solid body with a fluid (liquid or gas). It is not generated by a force field, in the sense of a gravitational field or an electromagnetic field, where one object can affect another object without being in physical contact.
For drag to be generated, the solid body must be in contact with the fluid. If there is no fluid, there is no drag. Drag in aircraft is generated by the difference in velocity between the solid object and the fluid. There must be motion between the object and the fluid. If there is no motion, there is no drag. It makes no difference whether the object moves through a static fluid or whether the fluid moves past a static solid object.
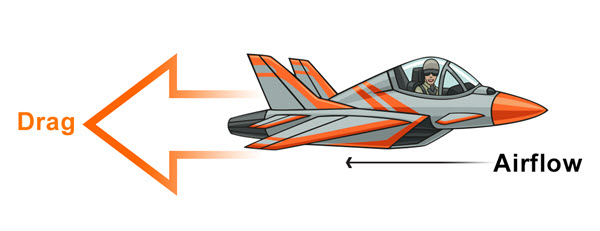
Drag is a force and is therefore a vector quantity having both a magnitude and a direction. Drag acts in a direction that is opposite to the motion of the aircraft. Lift acts perpendicular to the motion. There are many factors that affect the magnitude of the drag. Many of the factors also affect lift but there are some factors that are unique to aircraft drag. Drag must be overcome by thrust in order to achieve forward motion.
Types Of Drag In Aircraft:
1. Parasitic Drag
- Form Drag
- Interference Drag
- Skin Friction Drag
2. Induced Drag
3. Wave Drag
1. Parasitic Drag:
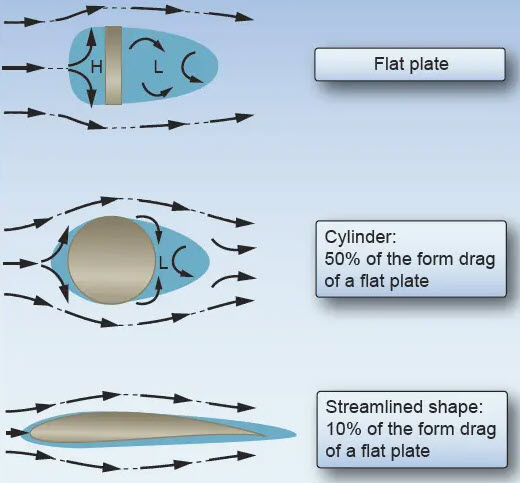
Form Drag:
Form or pressure drag is caused by the air that is flowing over the aircraft or airfoil. The separation of air creates turbulence and results in pockets of low and high pressure that leave a wake behind the airplane or airfoil (thus the name pressure drag). This opposes forward motion and is a component of the total drag. Since this drag is due to the shape or form of the aircraft, it is also called form drag. Streamlining the aircraft will reduce form drag.
Airplane components that produce form drag includes,
- Wing and wing flaps
- Fuselage
- Tail surfaces
- Nacelles
- Landing gear
- Wing tanks and external stores
- Engines
The easiest way to understand this drag is by having our hand out of the car window. When your hand is horizontal like an airfoil, it’s easy to stick outside the window. But when you open your hand into the wind, your hand flies backwards, and requires a lot more force to hold it position. That’s the easiest way to understand form drag.
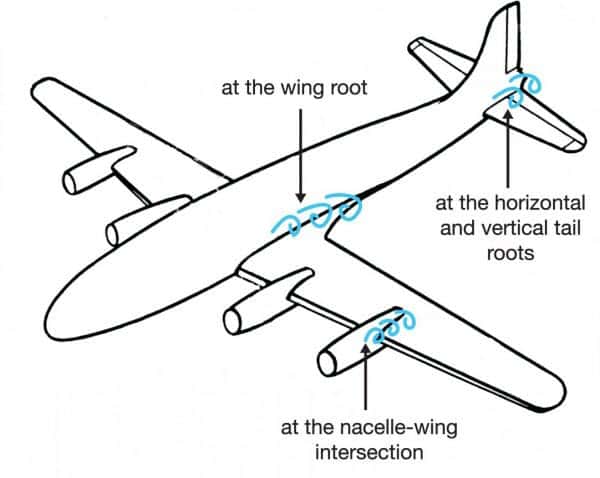
Interference Drag:
Interference drag comes from the intersection of air streams that creates eddy currents, turbulence, or restricts smooth airflow. For example, the intersection of the wing and the fuselage at the wing root has significant interference drag. It is also very high when two surfaces meet at perpendicular angles.
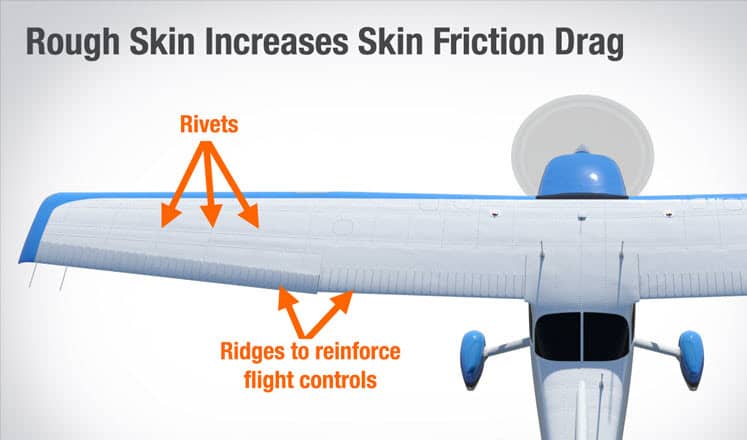
Skin Friction Drag:
Skin friction drag is caused by the actual contact of the air particles against the surface of the aircraft. This is the same as the friction between any two objects or substances. Because skin friction drag is an interaction between a solid (the airplane surface) and a gas (the air), the magnitude of skin friction drag depends on the properties of both the solid and the gas. For the solid airplane, skin fiction drag can be reduced, and airspeed can be increased somewhat, by keeping an aircraft’s surface highly polished and clean.
2. Induced Drag:
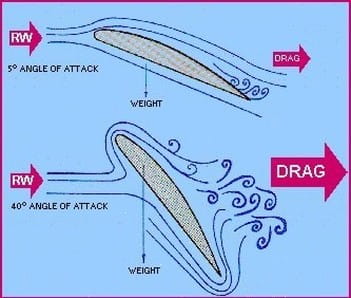
Induced drag is the drag created by the vortices at the tip of an aircraft’s wing. Induced drag is the drag due to lift. The high pressure underneath the wing causes the airflow at the tips of the wings to curl around from bottom to top in a circular motion. This results in a trailing vortex. Induced drag increases in direct proportion to increases in the angle of attack. The circular motion creates a change in the angle of attack near the wing tip which causes an increase in drag. The greater the angle of attack up to the critical angle (where a stall takes place), the greater the amount of lift developed and the greater the induced drag.
3. Wave Drag:
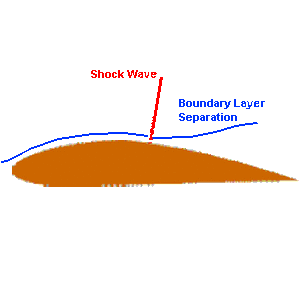
Wave drag is caused by the formation of shock waves around the aircraft in transonic or supersonic flight. As air flows from the supersonic region in front of the shockwave, to the subsonic region behind the shockwave, it separates and becomes turbulent. As the shockwave becomes stronger, more airflow separation occurs, known as wave drag.
To find more topics on our website…
Do you want to refer wikipedia? Please click here…
