# RAMJET ENGINE:
Table of Contents:
- What Is Ramjet Engine?
- Operating Principles Of Ramjet Engine
Critical
Subcritical
Supercritical - Explanation With Respect To Pressure Recovery And Mass Flow Rate Of Air
- Advantages Of Ramjet Engine
- Disadvantages Of Ramjet Engine
What Is Ramjet Engine?
A ramjet, sometimes referred to as a flying stovepipe or an athodyd (aero thermodynamic duct), is a form of airbreathing jet engine that uses the engine’s forward motion to compress incoming air without an axial compressor or a centrifugal compressor. Because ramjets cannot produce thrust at zero airspeed, they cannot move an aircraft from a standstill. A ramjet-powered vehicle, therefore, requires an assisted take-off like a rocket assist to accelerate it to a speed where it begins to produce thrust.
Ramjets work most efficiently at supersonic speeds around Mach 3 (2,300 mph; 3,700 km/h). This type of engine can operate up to speeds of Mach 6 (4,600 mph; 7,400 km/h). Ramjets can be particularly useful in applications requiring a small and simple mechanism for high-speed use, such as missiles. As speed increases, the efficiency of a ramjet starts to drop as the air temperature in the inlet increases due to compression. As the inlet temperature gets closer to the exhaust temperature, less energy can be extracted in the form of thrust.
To produce a usable amount of thrust at yet higher speeds, the ramjet must be modified so that the incoming air is not compressed (and therefore heated) nearly as much. This means that the air flowing through the combustion chamber is still moving very fast (relative to the engine), in fact it will be supersonic—hence the name supersonic-combustion ramjet, or scramjet.
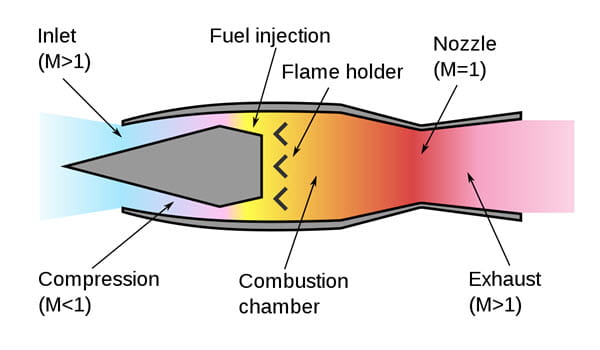
Operating Principles Of Ramjet Engine:
A discussion of a ramjet engine can be simplified by assuming that the ramjet is stationary, and that air approaches the engine at a velocity equal to the vehicle speed. As air enters the inlet, adiabatic compression causes an increase in temperature and a decrease in velocity. The air is further heated by combustion of the fuel which also increases the mass flow, typically between 5 and 10%. The high-temperature compressed gases are then expanded in the nozzle and accelerated to high velocity.
The thrust developed by the engine is the net rate of change of momentum of the gases passing through the engine and is equal to the mass flow rate of the air plus burned fuel times the jet velocity minus the flow rate of air times the air velocity. The effective net thrust on the vehicle will be somewhat less than the engine thrust because of skin friction drag on the air flowing around the ramjet vehicle. There are three distinct conditions under which a ramjet engine diffuser can operate, depending on the heat released in the combustor.
- Critical
- Subcritical
- Supercritical
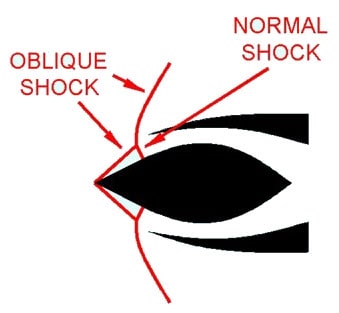
1. Critical (Ramjet Engine):
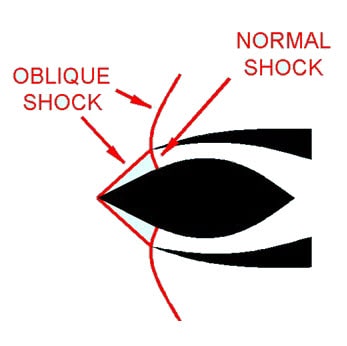
2. Subcritical (Ramjet Engine):
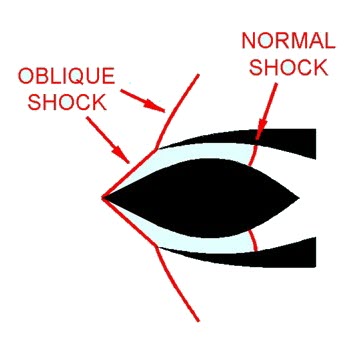
3. Supercritical (Ramjet Engine):
Explanation With Respect To Pressure Recovery And Mass Flow Rate Of Air:
- The condition of maximum pressure recovery at maximum mass flow rate is termed the critical point or critical operation.
- Operation at a lower flow rate is called subcritical operation.
- Operation at maximum flow rate but lower pressure recovery is termed supercritical operation.
Advantages Of Ramjet Engine:
- High temperatures can be employed.
- In the absence of rotating machinery, its construction is very simple and cheap.
- It can operate efficiently at high supersonic Mach numbers.
- It is not very sensitive to the quality of fuel.
- It provides high thrust per unit weight.
Disadvantages Of Ramjet Engine:
- It requires a launching device at supersonic speed.
- It is unsuitable for subsonic speeds.
- It has low thermal efficiency and high TSFC.
- Its maximum operating altitude is limited.
